Member-only story
Graph Representations: A Comprehensive Guide
In this post, we will look at various graph representations and how to translate the representation to the code in Java.
Graph Representation
In order to represent a graph in code, you have to store information about
- The Vertices which are part of the given Graph and,
- The Edges which connect vertices
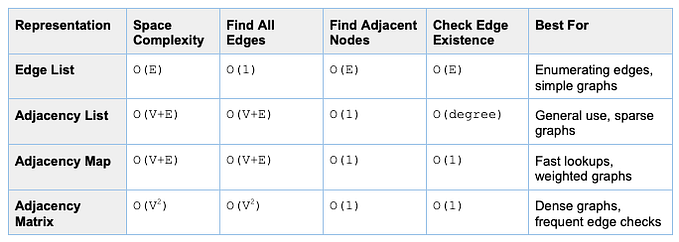
Graphs can be represented in various ways in programming. The most common representations are: Adjacency Matrix, Adjacency List and Edge List
Adjacency Matrix Representation of Graphs
An adjacency matrix is a 2D array used to represent a graph. In this representation, the graph is described by a square matrix A of size V x V where V is the number of vertices. Each element A[i][j] indicates whether there is an edge from vertex i to vertex j.
Characteristics
- Storage: Uses
O(V2)space, whereVis the number of vertices. - Edge Presence:
A[i][j] = 1if there is an edge from vertexito vertexj, otherwiseA[i][j] = 0. - Weighted Graphs: For weighted graphs,
A[i][j]can store the weight of the edge. - Use Case: Efficient for dense graphs where the number of edges
Eis close toV2, and for quickly checking the presence of edges.
Example
Consider a simple undirected graph with 4 vertices (0, 1, 2, 3) and 4 edges:
Adjacency Matrix Representation
The adjacency matrix for this graph would be:
Java Implementation
Here’s how you can represent and print an adjacency matrix in Java:
// Class to represent a graph using adjacency matrix
class Graph {
private final int[][] adjMatrix;
private final int V;
// Constructor
public Graph(int V) {
this.V = V;
adjMatrix = new int[V][V];
}
// Method to add an edge to the graph
public void addEdge(int src, int dest) {…